Maximize Battery Life with Electrent’s Home Inverter: Boost Charge, Cut-Off Voltage, and Advanced Charging Stages
Share
The Benefits of Electrent’s Home Inverter: Boost Charge, Cut-Off Voltage, and More
Inverters play a vital role in many areas, from keeping your home powered during outages to supporting renewable energy setups. They take the direct current (DC) from your batteries and transform it into alternating current (AC), the type of power used by most appliances and equipment. To keep your power flowing smoothly and reliably, an inverter needs to handle both charging and discharging efficiently. In this blog, we'll explore how Electrent’s advanced inverter technology can make a difference and break down the key things you need to know about how charging works.
Electrent Home Inverter: Modern Technology for Efficient Power Management
Electrent Home Inverter is engineered with advanced features designed to enhance battery performance and extend its lifespan. Here’s how it manages the charging process:
1. Boost Charge Feature:
- Boost Charge: The inverter increases the voltage to 14.5V for 5 minutes before returning to and maintaining 13.6V. This feature is crucial for extending battery life by 12 to 24 months, ensuring reliable backup even after 5 years.
- Activation: If the battery voltage falls below 12.3V (due to usage or other reasons), the inverter activates its boost charge feature.
2. Charging Cut-Off Voltage:
- Voltage: The inverter maintains a precise cut-off voltage of 13.6V.
- Trickle Current: Once 13.6V is reached, the trickle current drops to zero. To maintain this voltage, the current can go up to a maximum of 3 amps. This feature ensures optimal battery charge without unnecessary power consumption.
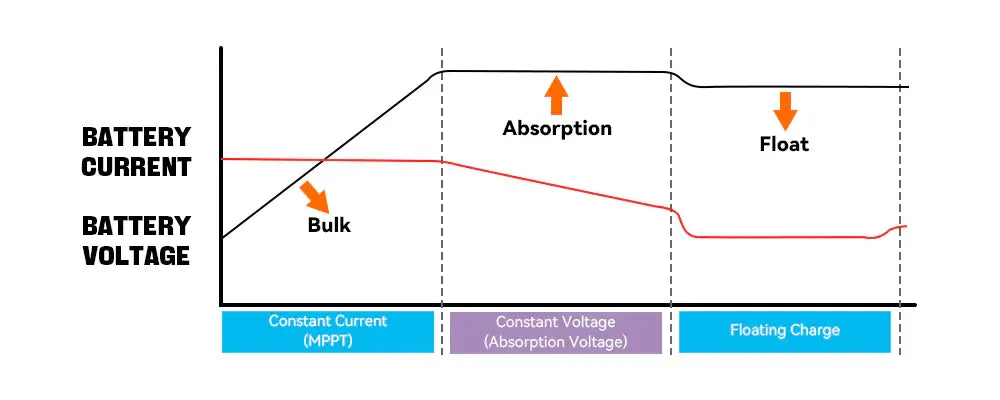
The Three Stages of Battery Charging: What You Need to Know
For those interested in the technical aspects of inverters, understanding the charging process is essential:
1. Bulk Charge:
- Purpose: Rapidly charges the battery to bring it to a near-full state.
- Typical Voltage: For a 12V system, the voltage ranges from 14.4V to 14.8V.
2. Absorption Charge:
- Purpose: Ensures the battery is fully charged by gradually reducing the current as it nears full charge.
- Typical Voltage: Maintains the same voltage range as the bulk charge phase.
3. Float Charge:
- Purpose: Maintains the battery at full charge without overcharging.
- Typical Voltage: For a 12V system, the float charge voltage ranges from 13.2V to 13.8V.
Explore our range of Elect Pure Sine Wave UPS inverter to find the perfect
